Mastering Six Sigma: Strategies, Implementation, and Success Stories in Business
Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology that aims to improve the quality of processes by identifying and removing defects and variations. Originating from Motorola in the 1980s and popularized by companies like General Electric (GE), Six Sigma has become a widely adopted approach to enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, and drive customer satisfaction. This article provides an in-depth exploration of Six Sigma, its implementation, and examples of companies that have successfully integrated it into their operations.
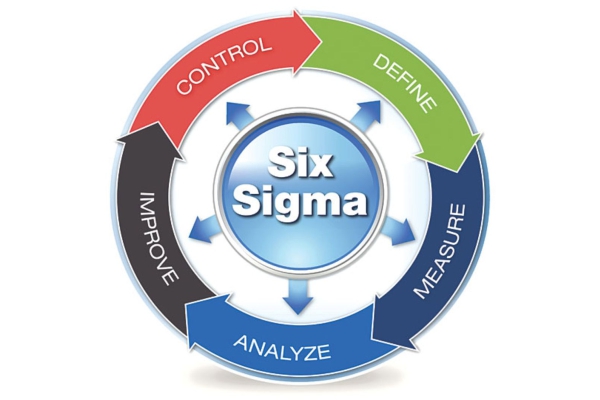
Understanding Six Sigma: At its core, Six Sigma is based on a set of principles and methodologies focused on achieving near-perfect performance in processes. Central to Six Sigma is the DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) methodology, which serves as a structured approach for process improvement. Let's delve deeper into each phase:
- Define: In this phase, the project goals and customer requirements are clearly defined. Project scope, objectives, and deliverables are established, laying the groundwork for the improvement process.
- Measure: Once the project is defined, data is collected to assess the current state of the process. Key performance indicators (KPIs) are identified and measured to quantify the process performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Analyze: In the analysis phase, data is analyzed to identify root causes of defects or variations in the process. Various statistical tools and techniques, such as Pareto charts, cause-and-effect diagrams, and hypothesis testing, are employed to pinpoint factors contributing to process inefficiencies.
- Improve: Based on the findings from the analysis phase, solutions are developed and implemented to address identified root causes. The focus is on implementing changes that will lead to significant improvements in process performance while minimizing risks.
- Control: The final phase of DMAIC involves establishing control mechanisms to sustain the improvements achieved. Control measures, such as process monitoring, standardization of procedures, and employee training, are put in place to ensure that the process remains stable and continues to meet performance goals.
- Implementation of Six Sigma: Successful implementation of Six Sigma requires strong leadership commitment, adequate resources, and a culture of continuous improvement. Here are key steps involved in implementing Six Sigma within an organization:
- Leadership Commitment: Top management support is essential for the successful adoption of Six Sigma. Leaders must champion Six Sigma initiatives, allocate resources, and empower employees to drive process improvement efforts.
- Training and Education: Training programs are conducted to equip employees with the necessary skills and knowledge to apply Six Sigma methodologies effectively. Certification programs, such as Green Belt and Black Belt, are available to train individuals at different levels of expertise.
- Project Selection: Projects are selected based on their alignment with organizational goals, potential impact on business outcomes, and availability of data for analysis. Cross-functional teams are formed to lead and execute Six Sigma projects.
- Data-Driven Approach: Six Sigma relies on data and statistical analysis to identify root causes of problems and validate improvement efforts. Organizations must invest in data collection systems and analytical tools to support the Six Sigma process.
- Continuous Improvement: Six Sigma is not a one-time initiative but a continuous journey towards excellence. Organizations must foster a culture of continuous improvement, where employees are encouraged to seek out opportunities for optimization and innovation.

Examples of Companies Following Six Sigma: Several companies across various industries have embraced Six Sigma principles and achieved significant success. Here are examples of companies known for their successful implementation of Six Sigma:
- General Electric (GE): GE is often cited as a pioneer in Six Sigma implementation. Under the leadership of Jack Welch, GE utilized Six Sigma to drive quality improvements, streamline processes, and enhance customer satisfaction.
- Motorola: Motorola was one of the first companies to develop and implement Six Sigma methodologies. Six Sigma played a crucial role in Motorola's transformation into a quality-driven organization, leading to substantial cost savings and competitive advantages.
- Toyota: While Toyota is more commonly associated with the Toyota Production System (TPS), the company has also integrated Six Sigma principles into its operations. Toyota leverages Six Sigma to identify and eliminate waste, improve efficiency, and deliver high-quality products to customers.
- Amazon: Amazon has successfully applied Six Sigma methodologies to optimize its logistics and supply chain operations. By leveraging data analytics and process improvement techniques, Amazon has been able to enhance delivery speed, accuracy, and customer satisfaction.
- Ford Motor Company: Ford Motor Company implemented Six Sigma to improve product quality and reduce defects in its manufacturing processes. Six Sigma initiatives at Ford led to substantial improvements in vehicle reliability, customer satisfaction, and cost savings.
Conclusion: Six Sigma offers a systematic approach to process improvement, enabling organizations to achieve higher levels of efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction. By implementing Six Sigma methodologies, companies can identify and eliminate defects, reduce variation, and drive continuous improvement across their operations. Through strong leadership commitment, rigorous training, and a data-driven approach, organizations can harness the power of Six Sigma to achieve sustainable business success.



 336
336

 The BharatBiz
The BharatBiz
 16
16

